Busbars function as the skeleton of a photovoltaic (PV) cell, allowing the entire cell to generate power. The current generated in a crystalline silicon cell is predominantly extracted through metal electrodes, which are classified into main busbars and auxiliary busbars (also known as fine busbars). The main busbars are primarily used to gather current and connect the auxiliary busbars in series, whilst the auxiliary busbars collect photogenerated carriers.
The evolution of solar cell technology has been marked by significant advancements, particularly in the design and functionality of busbars. The latest developments in Multi-Busbar (MBB solar cell), Super Multi-Busbar (SMBB solar cell), and Zero Busbar (0BB solar cell) technologies are reshaping the photovoltaic (PV) landscape, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving reliability.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Busbar Technology
Busbars serve as the backbone of photovoltaic cells, facilitating the collection and conduction of electric current generated by solar energy. Traditionally, solar cells utilized a limited number of busbars (2 to 5). However, advancements have led to the introduction of MBB technology, which employs 9 or more busbars, significantly enhancing the performance of solar cells.
Multi-Busbar (MBB) Technology
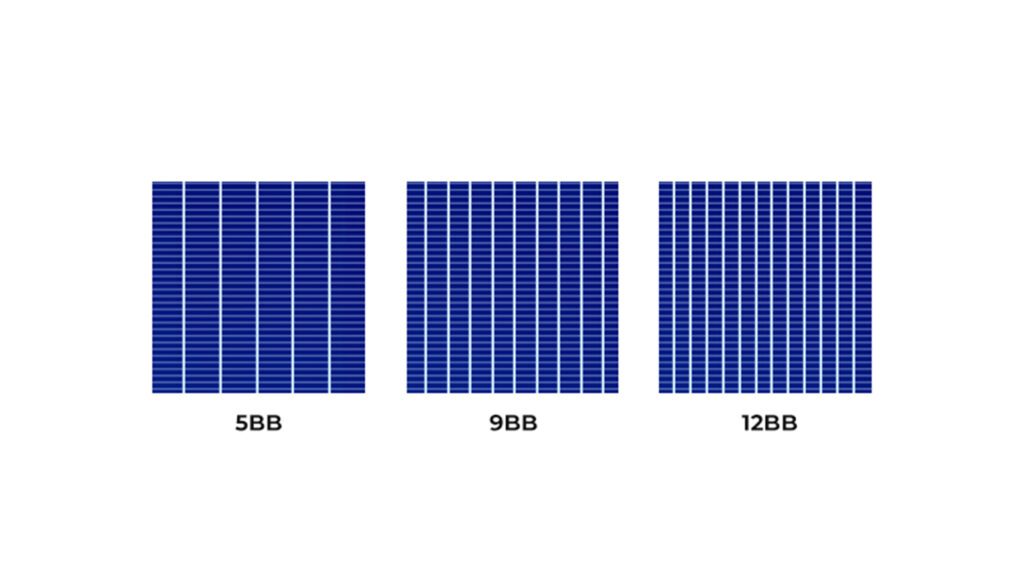
MBB technology is essential for improving solar cell efficiency. By increasing the number of busbars, MBB technology reduces resistive losses and enhances the fill factor, leading to better overall efficiency. Key advantages include:
Increased Number of Busbars
Conventional solar cells typically have 2-5 busbars, while MBB technology incorporates 9 or more busbars. The higher number of busbars reduces the spacing between them, resulting in a shorter current path in both the fingers and busbars. This effectively lowers series resistance losses, improving the fill factor and overall efficiency.
Also read: Discover the Best Solar Panels for Soil-less Farming Today!
Reduced Silver Consumption
The multi-busbar design allows for the use of thinner fingers, which decreases shading on the cell surface. This enables more light to reach the silicon, increasing conversion efficiency. Additionally, the reduced silver paste usage can lead to cost savings of 50-80%.

Improved Mechanical Strength and Reliability
The increased number of busbars provides greater structural integrity to the solar cell, making it more resistant to damage during handling and installation. MBB cells are also more tolerant to micro-cracks and fractures, which can occur during production or installation, enhancing the long-term durability and reliability of the solar panel.
Book SMBB, 0BB and MBB Solar Cells
Enhanced Bifacial Properties
For bifacial PERC cells, MBB technology can improve the ratio of front power to rear power. By utilizing the multi-busbar technique, the shading towards the rear side decreases, and the bifacial light-harvesting function is enhanced.
Improved Aesthetics
The thinner fingers and increased number of busbars in MBB solar panels create a more visually appealing appearance compared to traditional solar panels.In summary, Multi-Busbar technology is a significant advancement in solar cell design, offering higher efficiency, reduced costs, improved reliability, and better aesthetics. As the demand for high-performance solar panels continues to grow, MBB technology is expected to play a crucial role in the future of the photovoltaic industry.
Super Multi-Busbar (SMBB) Technology
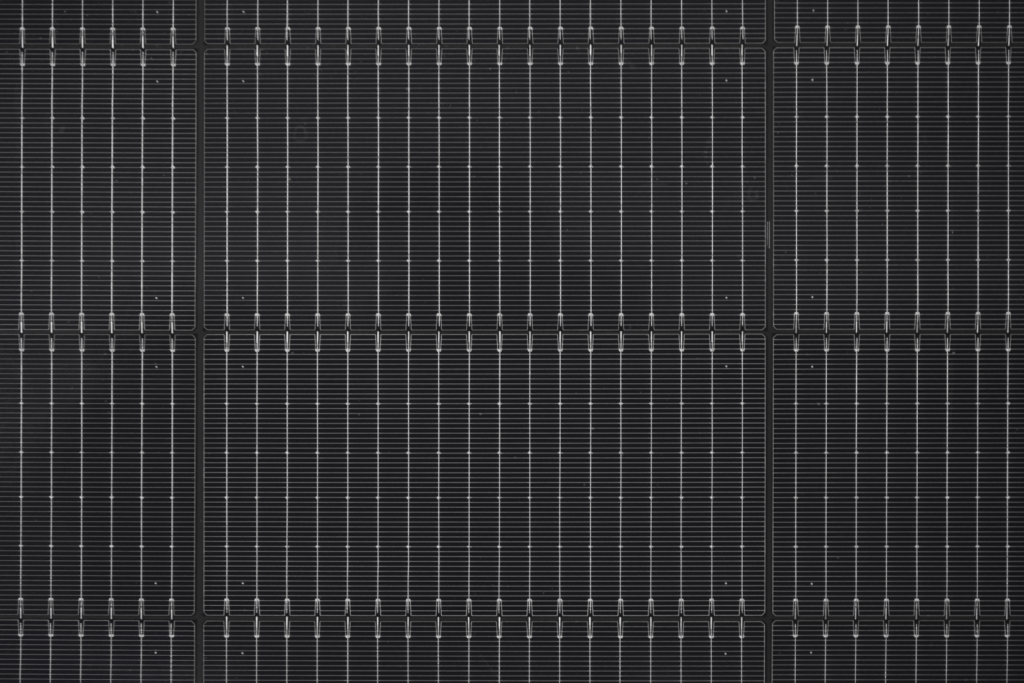

Super Multi-Busbar (SMBB) technology is an advanced solar cell design that enhances the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic (PV) systems. Building on the foundations established by Multi-Busbar (MBB) technology, SMBB incorporates a greater number of busbars, typically ranging from 16 to 25, to optimize current collection and reduce electrical losses.

Advantages of SMBB Technology
- Increased Number of Busbars:
SMBB technology utilizes a higher density of busbars compared to traditional designs. This significant increase allows for better current distribution across the solar cell, minimizing resistive losses and enhancing overall efficiency. - Finer Busbars:
The use of thinner busbars in SMBB reduces the shading effect on the solar cell surface. This design choice enables more sunlight to reach the active areas of the cell, thus improving light absorption and energy conversion. - Improved Shading Tolerance:
With more pathways for current flow, SMBB technology offers better performance in partially shaded conditions. The multiple busbars provide redundancy, ensuring that even if some areas of the cell are shaded, the overall output is less affected. - Reduced Series Resistance:
The arrangement of busbars in SMBB technology shortens the current transmission distances, which effectively lowers series resistance. This reduction in resistance translates to higher energy yields and improved efficiency. - Enhanced Reliability:
The increased number of busbars improves the mechanical strength of the solar cells, making them more resilient to micro-cracks and fractures that can occur during manufacturing or installation. This durability contributes to the longevity and reliability of the solar panels. - Cost Efficiency:
While the initial investment for SMBB technology may be higher due to advanced manufacturing processes, the reduction in silver paste usage and improved efficiency can lead to lower overall production costs and higher returns on investment.
Also read: What is TOPCon Technology Solar Cell?
Zero Busbar (0BB) Technology
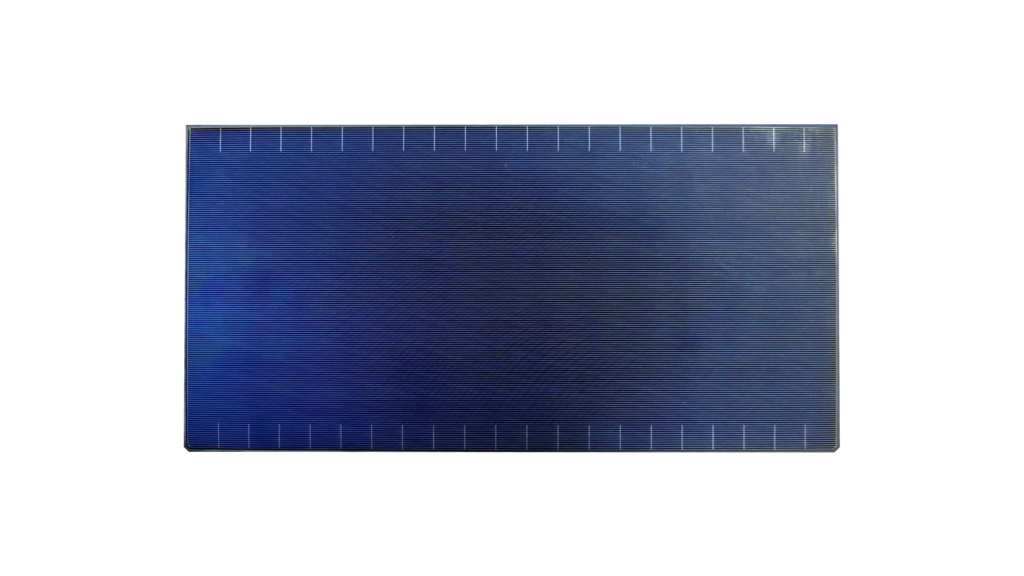
Zero Busbar (0BB) technology represents a significant advancement in solar photovoltaic (PV) cell design by eliminating traditional busbars, which are metal strips used to conduct electricity in solar panels. This innovative approach enhances solar cell efficiency, durability, and aesthetics, making it a game-changer in the solar energy industry.
Advantages of 0BB Technology
- Increased Efficiency: The absence of busbars minimizes shading, allowing for greater light absorption and improved energy conversion efficiency.
- Enhanced Reliability: With reduced mechanical stress and fewer components, 0BB technology enhances the reliability and longevity of solar panels.
- Cost Reduction: Significant savings in material usage, particularly silver, lead to lower manufacturing costs and more competitive pricing in the solar market.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The sleek design of busbar-free solar panels offers a more modern and visually appealing appearance, making them suitable for various architectural applications.
Conclusion
The advancements in MBB, SMBB, and 0BB technologies are pivotal in the ongoing evolution of solar energy solutions. Each technology builds upon the previous one, driving improvements in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
As the photovoltaic industry continues to grow, these innovations will play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of solar cells, contributing to the broader adoption of renewable energy sources.With companies like Maysun Solar leading the charge in developing high-quality photovoltaic modules, the future of solar energy looks promising, paving the way for more sustainable energy solutions globally.


